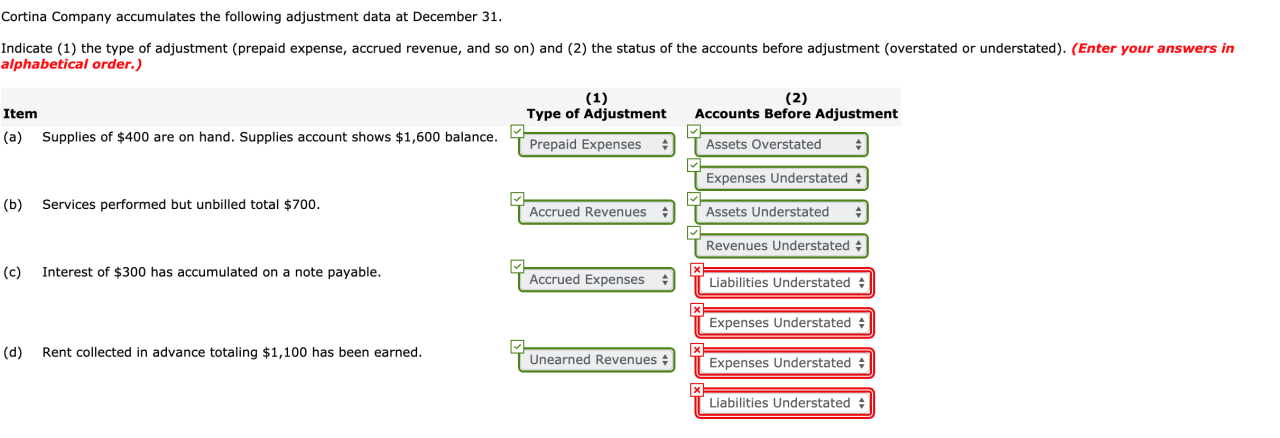
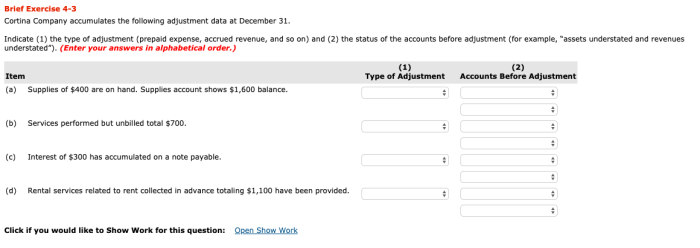
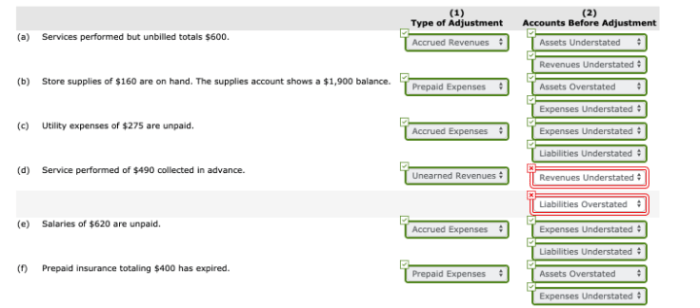
Cortina company accumulates the following adjustment data at december 31 – Cortina Company’s accumulation of adjustment data at December 31 provides valuable insights into the company’s financial performance. This detailed record of adjustments ensures accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards.
The adjustments encompass various aspects of the company’s operations, including depreciation, prepaid expenses, unearned revenue, inventory, and bad debts. Each adjustment plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the financial statements.
Adjustments to Accumulated Depreciation
Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset account that records the cumulative depreciation expense recognized on an asset over its useful life. It is deducted from the asset’s cost to determine its book value.
There are various methods used to calculate accumulated depreciation, including:
- Straight-line method
- Declining-balance method
- Units-of-production method
| Asset | Cost | Useful Life | Accumulated Depreciation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Building | $1,000,000 | 20 years | $200,000 |
| Equipment | $200,000 | 5 years | $80,000 |
| Vehicle | $50,000 | 3 years | $25,000 |
Adjustments to Prepaid Expenses: Cortina Company Accumulates The Following Adjustment Data At December 31
Prepaid expenses are assets that have been paid for but not yet consumed. They are initially recorded as assets and adjusted to expense as they are used.
Common examples of prepaid expenses include:
- Insurance premiums
- Rent
- Supplies
| Prepaid Expense | Balance at Beginning | Payments Made | Expenses Incurred | Balance at End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insurance | $6,000 | $2,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 |
| Rent | $12,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $12,000 |
| Supplies | $5,000 | $3,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 |
Adjustments to Unearned Revenue
Unearned revenue is a liability that represents advance payments received for services that have not yet been performed. It is initially recorded as a liability and adjusted to revenue as the services are performed.
There are two common methods used to record and adjust unearned revenue:
- Deferral method
- Accrual method
| Unearned Revenue | Balance at Beginning | Services Performed | Revenue Recognized | Balance at End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consulting Fees | $20,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Subscription Revenue | $15,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $10,000 |
| Ticket Sales | $10,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $4,000 |
Adjustments to Inventory
Inventory is a current asset that represents the goods held by a company for sale. It is important in financial reporting as it affects the calculation of cost of goods sold and gross profit.
There are various inventory costing methods, including:
- First-in, first-out (FIFO)
- Last-in, first-out (LIFO)
- Weighted average cost
The lower of cost or market (LCM) rule states that inventory should be valued at the lower of its cost or market value. This rule is applied to ensure that the inventory is not overstated on the balance sheet.
Adjustments to Bad Debts
Bad debts are uncollectible accounts receivable that are written off as a loss. There are various methods used to estimate bad debts, including:
- Percentage of sales method
- Aging method
| Customer | Balance at Beginning | Sales | Collections | Write-offs | Balance at End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | $1,000 | $2,000 | $1,500 | $500 | $1,000 |
| B | $500 | $1,000 | $800 | $200 | $500 |
| C | $200 | $500 | $300 | $200 | $200 |
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of accumulated depreciation?
Accumulated depreciation provides an accurate representation of the asset’s value over its useful life, ensuring that the company’s financial statements reflect the asset’s declining value due to wear and tear.
How does the adjustment for prepaid expenses impact the company’s financial statements?
The adjustment for prepaid expenses ensures that the company recognizes the portion of prepaid expenses that has been used during the accounting period, resulting in a more accurate representation of expenses incurred.
What is the purpose of adjusting unearned revenue?
Adjusting unearned revenue allows the company to recognize revenue only when it has been earned, preventing the overstatement of revenue in the financial statements.