Mutations Match the Words with Their Definition: An Exploration of Genetic Variations takes readers on an enthralling journey into the realm of genetics, uncovering the fascinating world of mutations and their profound impact on living organisms. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the concept of mutations, their diverse types, and their far-reaching consequences, both beneficial and detrimental.
Delving into the intricacies of genetics, we unravel the mechanisms underlying mutations, shedding light on their role in shaping the genetic makeup of individuals and driving the evolutionary process. Through engaging examples and clear explanations, we illuminate the intricate dance between mutations and the genetic code, exploring how these changes can alter gene function, protein structure, and ultimately the health and characteristics of organisms.
Mutation Definitions
Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA sequence of an organism. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental toxins, radiation, and errors during DNA replication. Mutations can have a wide range of effects, from being completely harmless to causing serious diseases or even death.
Types of Mutations
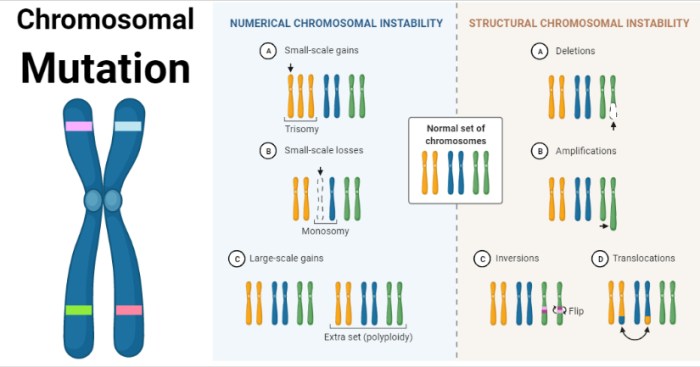
- Point mutationsare changes in a single nucleotide base pair.
- Insertionsare the addition of one or more nucleotides into a DNA sequence.
- Deletionsare the removal of one or more nucleotides from a DNA sequence.
- Inversionsare the reversal of the orientation of a segment of DNA.
- Translocationsare the movement of a segment of DNA from one chromosome to another.
Consequences of Mutations, Mutations match the words with their definition
The consequences of mutations can vary depending on the type of mutation and the location of the mutation in the DNA sequence. Some mutations are completely harmless, while others can cause serious diseases or even death. Mutations can affect gene function, protein structure, and overall organism health.
Matching Mutations to Definitions
| Mutation Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Point mutation | Change in a single nucleotide base pair |
| Insertion | Addition of one or more nucleotides into a DNA sequence |
| Deletion | Removal of one or more nucleotides from a DNA sequence |
| Inversion | Reversal of the orientation of a segment of DNA |
| Translocation | Movement of a segment of DNA from one chromosome to another |
Examples of Mutation Matches
- A point mutation in the BRCA1 gene can increase the risk of breast cancer.
- An insertion in the CFTR gene can cause cystic fibrosis.
- A deletion in the DMD gene can cause Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
- An inversion in chromosome 22 can cause cat eye syndrome.
- A translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 can cause chronic myeloid leukemia.
Elaborating on Mutation Consequences

Mutations can have a wide range of consequences, depending on the type of mutation and the location of the mutation in the DNA sequence. Some mutations are completely harmless, while others can cause serious diseases or even death.
Mutations can affect gene function by altering the sequence of amino acids in the protein that is encoded by the gene. This can lead to changes in the structure and function of the protein, which can have a variety of effects on the organism.
Mutations can also affect protein structure by altering the way that the protein is folded. This can lead to changes in the protein’s activity and stability, which can have a variety of effects on the organism.
Mutations can also affect overall organism health by altering the way that the organism develops and functions. This can lead to a variety of health problems, including birth defects, developmental disorders, and cancer.
Impact of Mutations on Evolution: Mutations Match The Words With Their Definition
Mutations are the ultimate source of genetic variation, which is the raw material for evolution. Mutations can create new alleles, which are different versions of genes. These new alleles can then be passed on to offspring through sexual reproduction.
Natural selection is the process by which organisms with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce than organisms with less advantageous traits. Mutations that provide an advantage to an organism are more likely to be passed on to offspring, while mutations that provide a disadvantage are less likely to be passed on.
Over time, natural selection can lead to the accumulation of advantageous mutations in a population. This can lead to the evolution of new species or the adaptation of existing species to new environments.
Top FAQs
What are mutations?
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence of an organism, which can arise from various factors such as environmental exposure, errors during DNA replication, or spontaneous chemical changes.
How can mutations be beneficial?
Beneficial mutations can provide organisms with new or improved traits that enhance their survival or reproductive success in their environment. For example, a mutation that confers resistance to a particular disease or allows an organism to adapt to a changing climate can be advantageous.
How can mutations be harmful?
Harmful mutations can disrupt gene function or alter protein structure, leading to genetic disorders, diseases, or reduced fitness. Examples include mutations that cause genetic diseases such as sickle cell anemia or cystic fibrosis.
What is the role of mutations in evolution?
Mutations are the ultimate source of genetic variation, providing the raw material for natural selection to act upon. By introducing new alleles into a population, mutations can drive evolutionary change and adaptation to new environments.